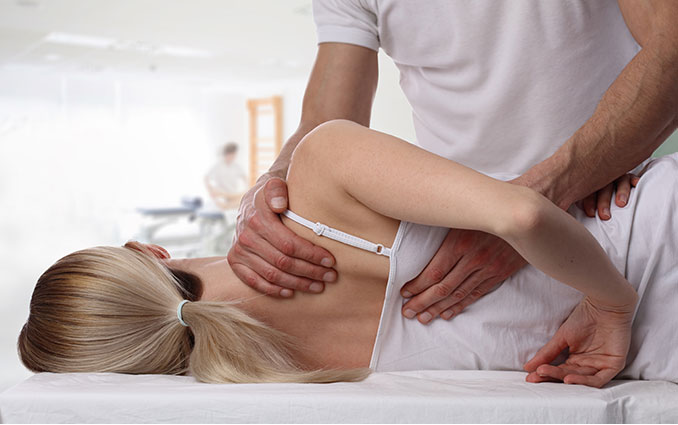
What Is Osteopathy?
Osteopathy is the combined application of manual therapy which recognizes the important link between the structure of the body and the way it functions. Osteopathy is the focus on how the skeleton, joints, muscles, nerves, circulation, connective tissue and internal organs function as a holistic unit.
Osteopathy is suitable for everyone: This includes newborn babies, children, teenagers, pregnant women, adults, the elderly, athletes, tradesmen, white collar, nurses, service and hospitality workers and more.
- Osteopaths are government registered practitioners who complete a minimum of five years’ university training in anatomy, physiology, pathology, general medical diagnosis and osteopathic techniques. They are primary healthcare practitioners and are trained to recognize conditions that may require medical referral. They are also trained to perform standard medical examinations of the musculoskeletal, cardiovascular, respiratory and nervous systems.
- Using skilled evaluation, diagnosis and a wide range of hands-on techniques, osteopaths can identify important types of dysfunction in your body.
- Our Osteopaths are covered by most private health funds and by Medicare’s Enhanced Primary Care (EPC) Plans. Osteopaths are registered providers for DVA patients, as well as by workers’ compensation schemes and motor accident insurers.
What does an Osteopathic treatment involve?
A typical consultation includes
- Taking a comprehensive case history
- Performing a thorough examination,
- Treatment using a combination of hands-on manual therapy
- Follow up and after care advise
All techniques are used with the aim to restore movement to areas of the body identified as being tight or restricted in movement. This enables the body to function at its optimal level which in turn allows healing to occur quickly.
Common techniques combined and used by your Osteopath include
- Soft tissue massage and stretching techniques
- Articulation/mobilisation techniquesthe movement of joints through their range of motion in order to restore function.
- High Velocity Low Amplitude techniques (HVLA)the technical term for manipulation, whereby the Osteopath uses a gentle method of maintaining precise positioning of a joint, followed by a mild thrust action.
- Muscle Energy techniques (MET)in which tight muscles are gently released by alternately being stretched and made to work against resistance. This helps to restore function to the muscles and surrounding joint structures.
- Counter-strain techniquesin which a release of restriction is achieved by the placement of the affected joint or muscle in a position of comfort, while applying a ‘counter’ stretch to the antagonists of the tight muscles.
- Functional techniqueswhereby the dysfunctional joint is placed into its preferred resting position, allowing a gentle release of the joint to occur.

Free Parking Available
Wheelchair Access
Close to Public Transport